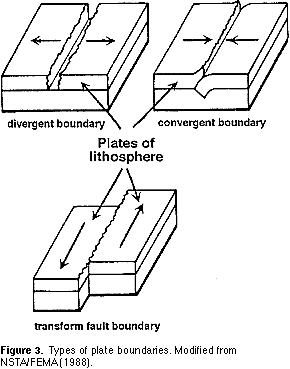
Seafloor spreading is the continuous process of forming new igneous rock at midocean ridges by injection of magma that forms new seafloor.
Characteristics of sea floor spreading sea floor spreading cartoon.
Maps and other data gathered during the war allowed scientists to develop the seafloor spreading hypothesis this hypothesis traces oceanic crust from its origin at a mid ocean ridge to its destruction at a deep sea trench and is the mechanism for continental drift.
The concept of sea floor spreading.
The motivating force for seafloor spreading ridges is tectonic plate pull rather than magma pressure although there is typically significant magma activity at spreading ridges.
Seafloor spreading happens at the bottom of an ocean as tectonic plates move apart.
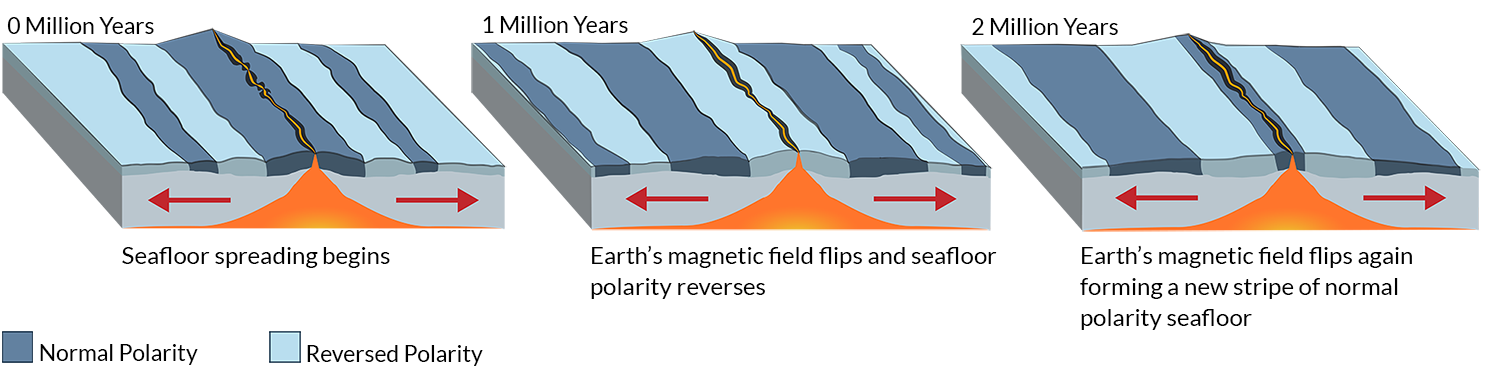
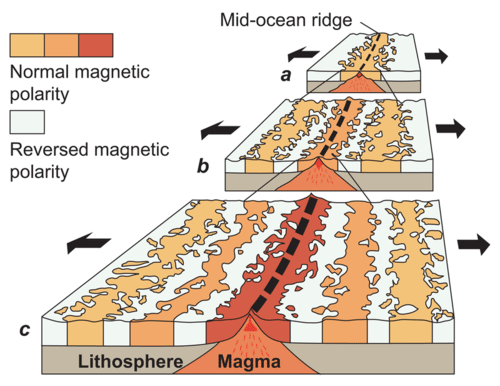
The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century.
See also continental drift a veritable legion of evidence supports the seafloor spreading hypothesis.
Hess called this processsea floor spreading.
Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
Subduction and sea floor spreading are processes that could alter the size and form of the ocean.
The process is continuous because forces cause opposite sides of the midocean ridge to constantly move apart making new room for the process to repeat.
Because of these processes the ocean floor is renewed about every 200 million years.
For instance the atlantic ocean is believed to be expanding because of its few trenches.
This diagram provides evidence of seafloor spreading by showing the ages of ocean floor in the atlantic and eastern pacific oceans.
The process of subduction and sea floor spreading can change the size and shape of the oceans.
Wherever continents are bordered by deep sea trench systems as in the pacific ocean the ocean floor is plunged downward underthrusting the continents and ultimately reentering and dissolving in earth s mantle from which it had originated.
That is the time it takes for new rock to form at the mid ocean ridge move atoss the ocean and sink into a trench.
The red colors are the youngest parts of the seafloor where fresh new crust is formed as lava seeps up from the deep interior of the earth at spreading ridges as new crust forms at these spreading ridges older crust colored green in the diagram moves away from.
Evidence for sea floor spreading this movement begins at the mid ocean ridge which forms along in a crack in the oceanic crust at the mid ocean ridge molten materials rise fromthe mantle and erupts the molten material spreads out pushing olderrock to both sides of the ridge.
The concept of seafloor spreading was put forward by h harry hess an american geologist.
At ridges in the middle of oceans new oceanic crust is created.
World war ii gave scientists the tools to find the mechanism for continental drift that had eluded wegener.
Further he claimed that continents would be pushed aside by the same forces that cause the ocean to grow.